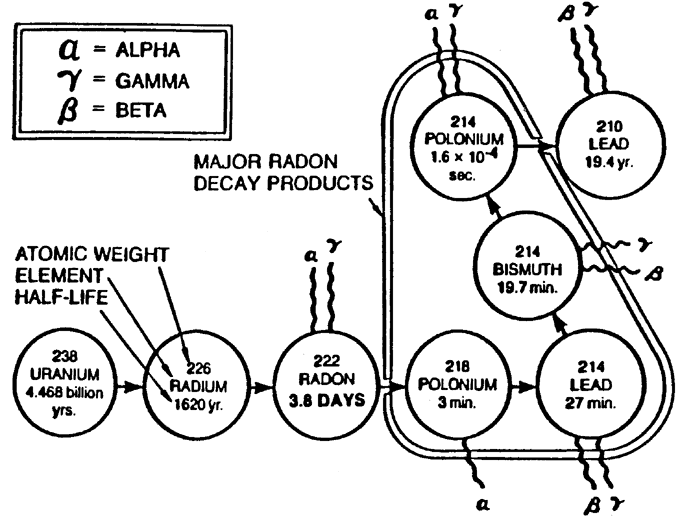
Below is a detailed chart showing the radioactivity pathway to radon from the original U-238 atom. Also shown are the different types of radiation:
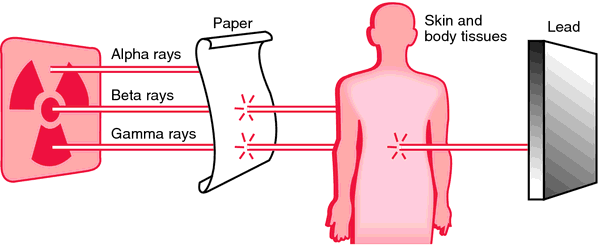
Alpha Radiation – (from Radon-222 as an example) high energy helium nuclei (almost no penetrating power, but does a great deal of damage at close range to cells and DNA – will not penetrate outer layer of skin, but can cause direct harm to epithelial cells in the lungs if inhaled) It causes approximately 5 X the damage of gamma Radiation or X-Rays.
Beta Radiation – high energy electron (much lighter than an alpha particle but it has a greater penetration)
Gamma Radiation – high energy photon (essentially without mass but has a high penetration factor through shielding)
If you follow the diagram below, the radioactive decay of Radon-222 to Lead-210 results in the emission of 3 alpha particles, 2 beta particles and a discrete amount of gamma radiation. (the nature of which is an electromagnetic wave, not a particle) Because radon decay products (RDPs) are electrically charged particles, they readily adhere to suspended dust particles (which can be inhaled) or other surfaces in a phenomena known as “plate-out”. Either pure RDPs or the particles they are attached to can be inhaled.