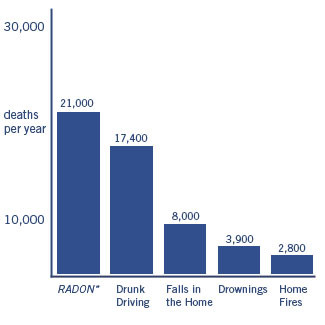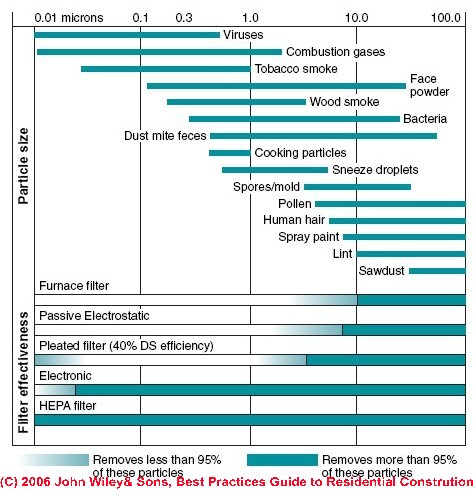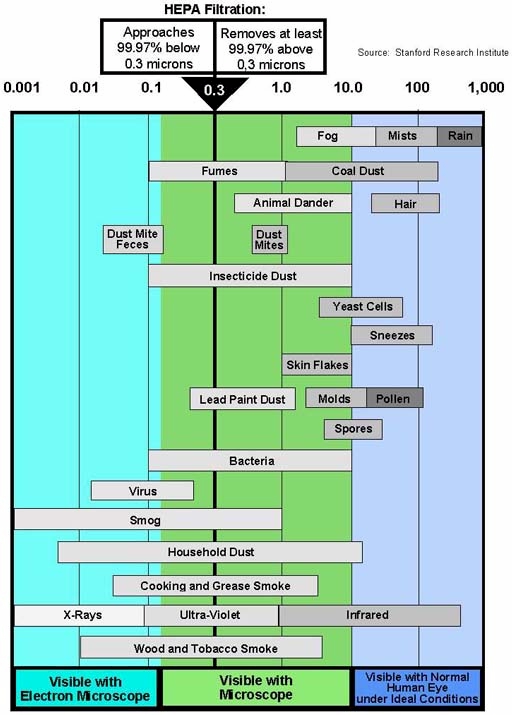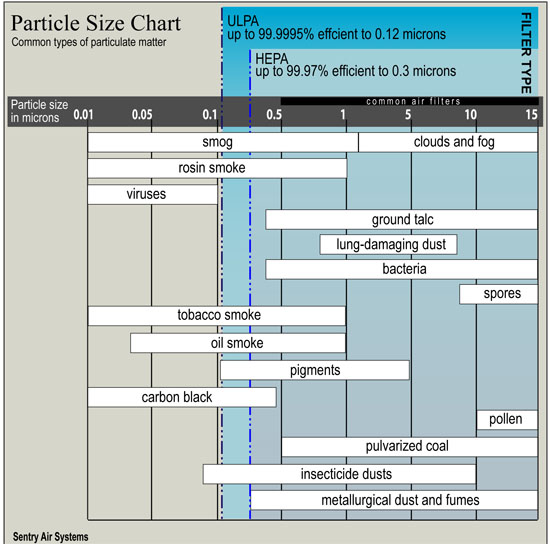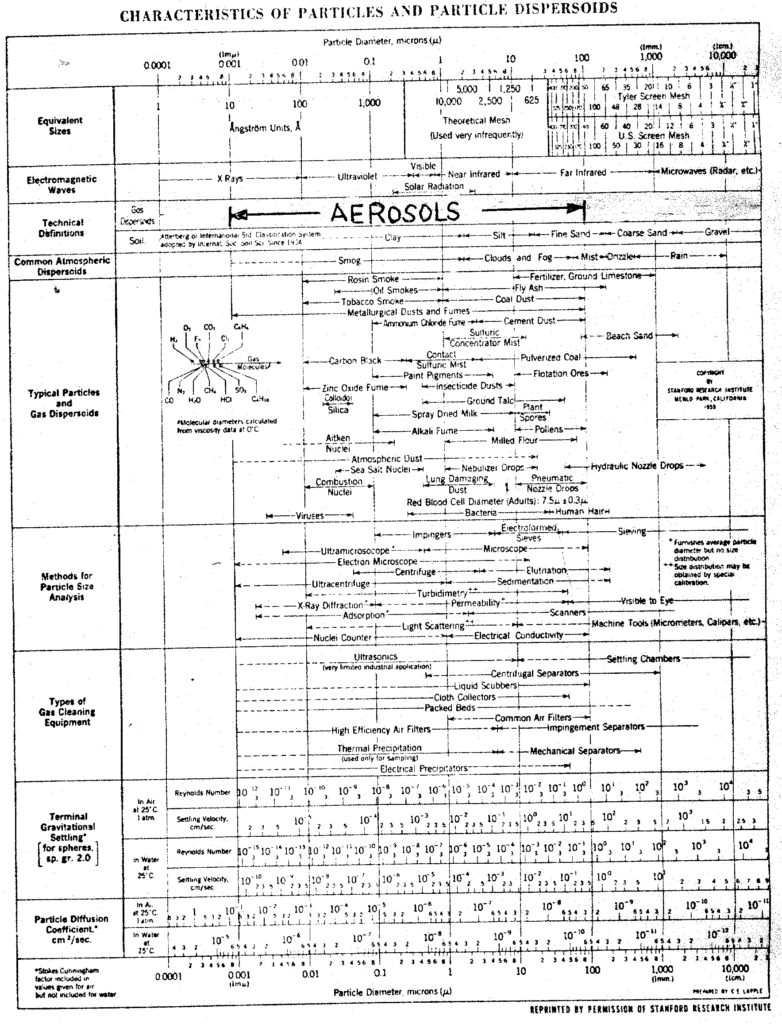
Radon gas in homes is one of the leading causes of lung cancer
- ScanTech does NOT perform residential testing for homeowners and tenants – all services are COMMERCIAL ONLY – HOMEOWNERS & RESIDENTIAL CLIENTS CLICK HERE
Current MAP requirements allow a 25% ground floor sampling variance from the ANSI-AARST testing protocol. However, if any of the units come back at or above 4 pCi/L, 100% ground floor testing is required. You can find the current radon policy in Chapter 9.5.C of the MAP guide: https://www.hud.gov/sites/documents/4430GHSGG-BM.PDF
Attached is a 2018 radon update from Pat Burke that supplements the existing policy: Radon Technical Updates Pat Burke November 2018
Multifamily has proposed eliminating the 25% sampling variance and requiring 100% ground floor testing. If approved, this change would go into effect when the new MAP guide is published. The guide is still going through review. (from a memo dated Aug 5th, 2020)
The new requirement has now largely passed and is in effect as of this writing (January 1st, 2022) and because of the ongoing pandemic, ScanTech is no longer performing surveys for OCCUPIED multi-family dwellings or nursing facilities. We only perform commercial surveys in unoccupied structures which are typically new builds, though we can still do office buildings under certain conditions such as in conjunction with other forms of indoor air quality testing.
Biomedical / Environmental Health & Safety Consulting & Field Testing With Industrial Hygiene & Microbiology expertise
Dallas Green Building Clearance Services – Certificate of Occupancy IAQ (Indoor Air Quality) VOC measurements for Dallas Green Building Ordinance Post-Construction with regards to Pre-Occupancy baseline IAQ testing Section 804.2.
In a rush to test your property for radon gas or radioactivity in natural stone such as granite or marble? Did you know that radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer? (Smoking is 1st and radon gas synergistically increases mortality rates for smokers)
While it is not well known, radon gas levels EXCEED EPA action limits of 4 picoCuries/liter (pCi/L) in up to 10 % of all homes in Dallas county with an additional 14 % falling into the marginal range of 2 – 4 pCi/L. This means that 1 out of 4 homes (10 % + 14 % = 24%) in Dallas either have a radon issue or fall into a caution category. Other counties, such as Tarrant, Collin and Denton are not immune either. (see the link below on Radon FAQ from ScanTech for more details)
Example areas of the Metroplex (not a complete or comprehensive list) which have been found by ScanTech testing to have excess radon levels which are statistically higher than the 24 % quoted above include:
- North Dallas and Far North Dallas
- Lake Highlands
- University Park
- Highland Park
- Park Cities area
- Richardson
- Arlington
ScanTech now has the capability to test and get results within as little as 24 hours of initial deployment using a high quality digital tester.
Our services are both faster and cheaper than competing methods or companies and we have been performing radon testing for homeowners in the DFW area for over 10 years.
Testing is performed by an engineering graduate experienced in radioactivity measurements, indoor air quality testing including mold inspection, formaldehyde and radon gas testing.

AARST-NRPP Nationally Certified Radon Residential Measurement Provider ID # 108991 RT* including Advanced Multi-Family & Large Buildings Radon Measurement MAMF-2017
*Meets HUD, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and GSA requirements
Mold Assessment Consultant – Texas Dept. of Health Service License # MAC1387 (now licensed by TDLR (Texas Dept. of Licensing & Registration)
(Activated charcoal short term radon test kits are accurate as well, but typically require at least 4 business days to get results under best case conditions and a complete kit deployment and pickup service is almost always more expensive due to the additional travel)
Call / text to 214.912.4691 – please include physical address, square footage property and email
More information is available here:
RADON FAQ Dallas /Fort Worth — DFW North Texas Area
http://www.indoorairqualitytestingdallas.com/
http://www.scantech7.com/formaldehyde-indoor-air-quality-testing-services-dallas-fort-worth/
Texas CMIS Mold Information Sheet
Cities for radon / air quality inspection services include: Dallas, Austin, Houston, San Antonio, Spring, The Woodlands, Round Rock, Plano, Highland Park, University Park, Park Cities, Arlington, Fort Worth, Grapevine, Frisco, Denton, McKinney, Allen, Lewisville, Irving, Mesquite, Bedford, Euless, Richardson, Coppell, Grand Prairie, Garland, Addison, Farmers Branch, Rockwall, Carrollton, Parker, Rowlett, Lucas, Fairview, Park Cities, Keller, Roanoke, The Colony, Highland Village, Lake Dallas, Corinth, Prosper, Duncanville, Lancaster, Rowlett, Royse City, Trophy Club, Southlake and Hurst. Counties served include Dallas, Collin, Denton, Tarrant and Rockwall County.
*LEGAL NOTICE*
All information on this website either written or implied is the express opinion of ScanTech Technical Consulting. ScanTech Technical Consulting and it’s owners are not responsible or liable for any damages arising from the misuse, misinterpretation or other consequences of the content of this website either in part or in whole. This includes all external weblinks, PDF documents, photos or other references (informational or otherwise) to 3rd parties including government agencies, health organizations, etc.
15770 Dallas Pkwy Suite # 900 Dallas, TX 75248 (Not Accepting Visitors due to C19)
Phone: (214).912.4691 https://emfsurvey.com
ScanTech Technical Consulting: Professional Electromagnetic EMF EMI Testing for Biomedical Implant & Equipment, Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Testing & Environmental Inspections
COPYRIGHT 2002 – 2022